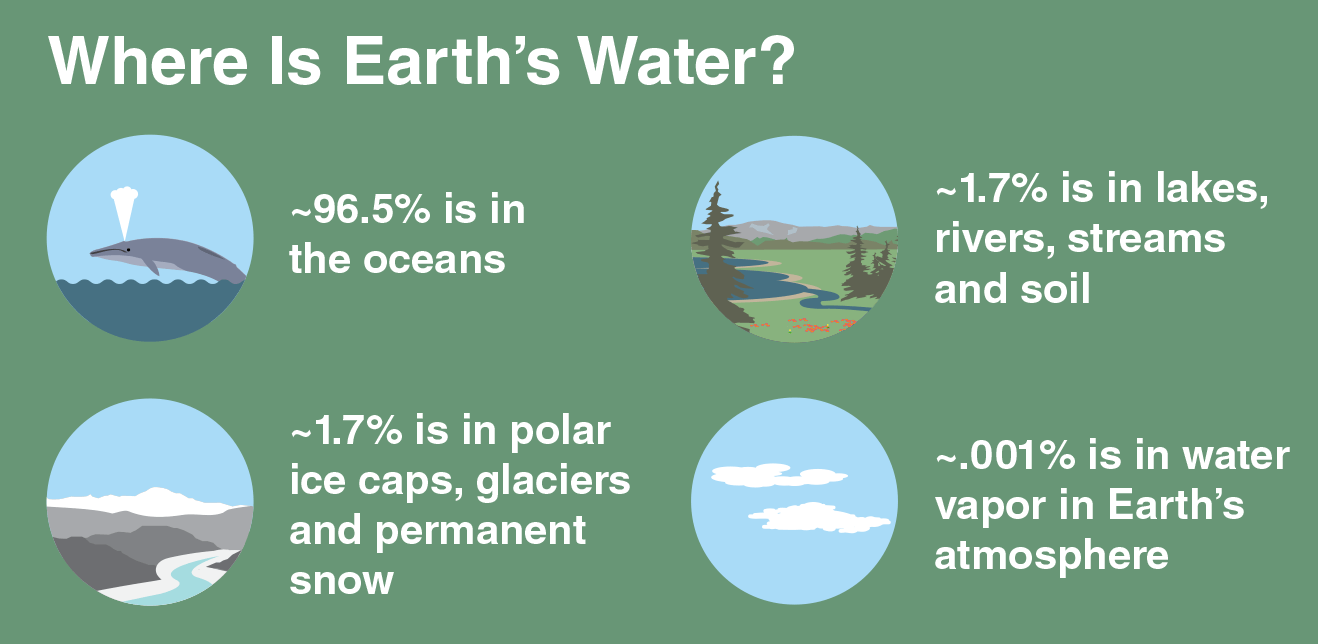
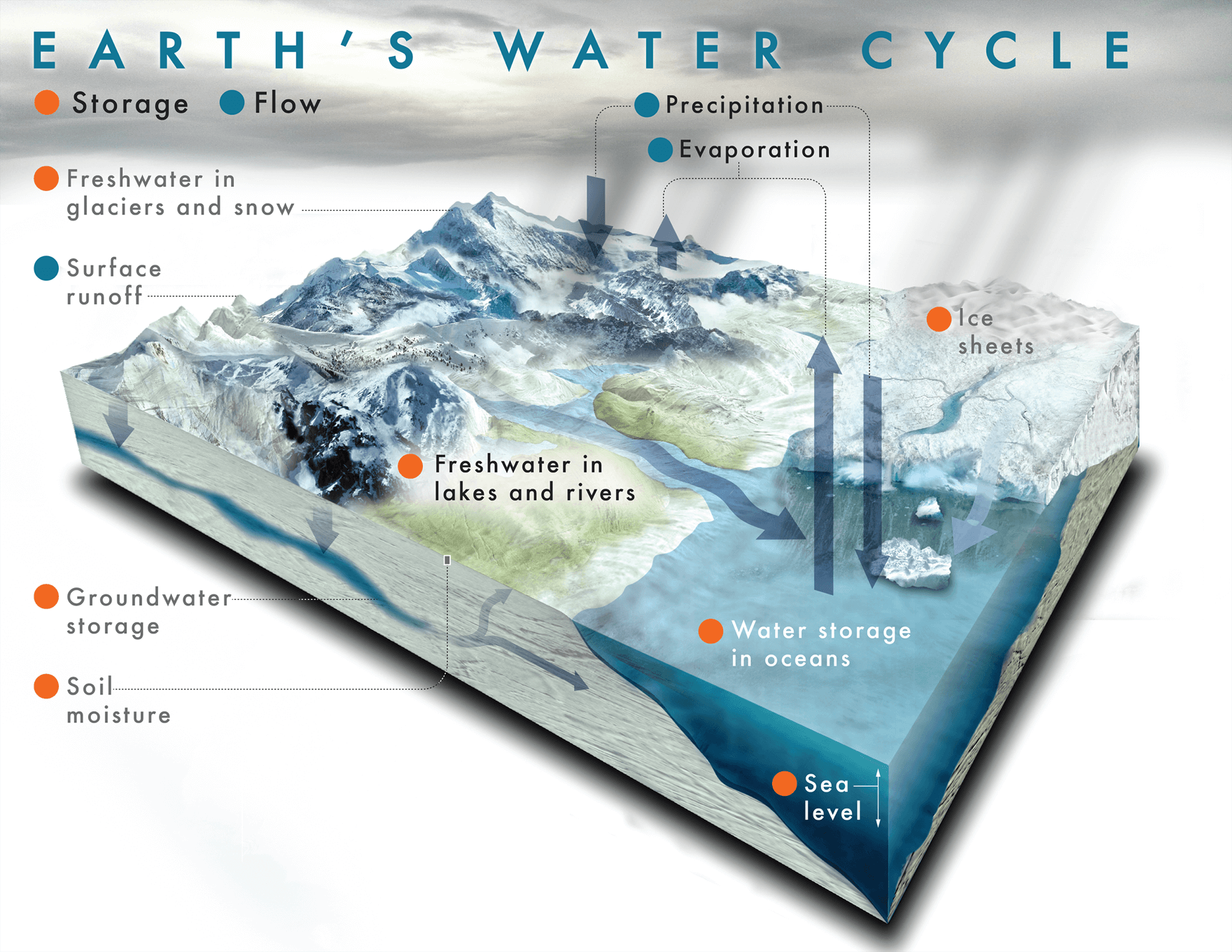
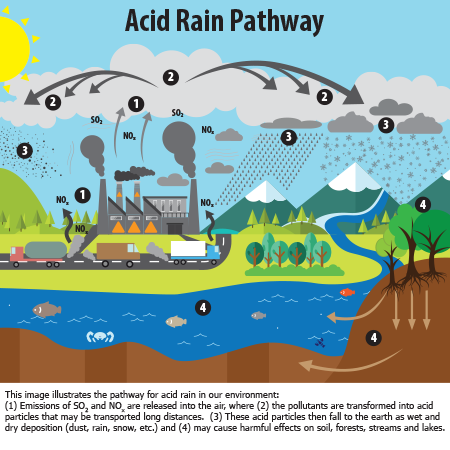
Aim: To learn practical ways of recycling so that we can make our world a better place.
How can we prevent climate change though recycling these products?
Plastics:So we dont need to use coal or electricity
Cycling or walking:so we dont need to use gas or oils
Paper:less cutting down trees
Steel:Not going to burn as much coal burning it and releasing CO2
What is Zero Waste?
Plastics:So we dont need to use coal or electricity
Cycling or walking:so we dont need to use gas or oils
Paper:less cutting down trees
Steel:Not going to burn as much coal burning it and releasing CO2
Video questions:
What is Zero Waste?
one of the quickest and cheapest ways a community can immediately reduce climate impact
What can we do on the planet?
What can we do on the planet?
- Reduse
- Reuse
- Recycle
- Repair
- Redesign
What do we need to recycle?
Plastic, Paper, Metal and Glass
What does recycling do?
prevents less CO2 being released into the air
How much of our rubbish is food scraps?
157,389 tonnes in New Zealand
What does soil do to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
absorb the CO2 and stores the CO2
absorb the CO2 and stores the CO2
What is a carbon footprint?
The amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere as a result of the activities of a particular individual, organization, or community.
How can you make your Carbon Footprint smaller?
not burn as much fossil fuel from factory and etc, also by sharing resorses and recycling.
ENERGY SAVING TIPS FILM
Name 4 of the tips.
- Solar Power
- reducing your rubbish that you put in the land fills
- Turning off switches to things your not using
- consuming less stuff
AT WHAT RATES DO DIFFERENT ITEMS DECOMPOSE?
MY INVESTIGATION.

Choose 5 items from the list and investigate them.
You need to answer three questions.
Name: News Paper
You need to answer three questions.
Name: News Paper
- How long do they take to decompose/ 2-4 weeks
- What resource / fossil fuel are they made from?Trees
- How is this resource recycled?It gets put in the yellow bins
- How does this object contribute to climate change?cutting down trees and releasing CO2 when they are getting burned
Name: orange Peels
- How long do they take to decompose?3-6 months
- What resource / fossil fuel are they made from? Trees
- How is this resource recycled?put it in the green bin
- How does this object contribute to climate change? cutting down trees and releasing CO2 when they are getting burned
Name:Plastic Bag
- How long do they take to decompose?10-20 years
- What resource / fossil fuel are they made from?oil
- How is this resource recycled?by putting it in the red bin
- How does this object contribute to climate change?fossil fuels are released when the plastic bags are being made
Name: Plastic 6 Pk Ring
- How long do they take to decompose?400-500 years
- What resource / fossil fuel are they made from?disposable packaging
- How is this resource recycled? by putting it in the recycling bin
- How does this object contribute to climate change?CO2 is being released by getting made
Name: Glass Bottle
- How long do they take to decompose?500-Forever
- What resource / fossil fuel are they made from?liquid sand
- How is this resource recycled?put in the recycling bin
- How does this object contribute to climate change?Releasing CO2 into the air by making it